System Architectures
Geo SCADA Knowledge Base
Access vast amounts of technical know-how and pro tips from our community of Geo SCADA experts.
Search in
Improve your search experience:
- Exact phrase → Use quotes " " (e.g., "error 404")
- Wildcard → Use * for partial words (e.g., build*, *tion)
- AND / OR → Combine keywords (e.g., login AND error, login OR sign‑in)
- Keep it short → Use 2–3 relevant words , not full sentences
- Filters → Narrow results by section (Knowledge Base, Users, Products)
-
database
32 -
Web Server and Client
31 -
WebX
19 -
Request Form
18 -
Lists, Events & Alarms
16 -
ViewX
15 -
Setup
12 -
Application Programming
12 -
Telemetry
8 -
Events & Alarms
7 -
Lists
7 -
Mimic Graphics
7 -
Downloads
6 -
Geo SCADA Expert
5 -
SCADA
5 -
IoT
5 -
Support
5 -
Drivers and Communications
4 -
Security
4 -
2025
3 -
IEC 61131-3 Logic
3 -
DNP 3
3 -
Virtual ViewX
2 -
Trends and Historian
2 -
Architectures
1 -
Templates and Instances
1 -
Releases
1 -
Maps and GIS
1 -
Mobile
1 -
Geo Scada
1 -
Tools & Resources
1 -
Privacy Policy
1 -
OPC-UA
1 -
ClearSCADA
1 -
Python
1
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Email to a Friend
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Link copied. Please paste this link to share this article on your social media post.
System Architectures
Originally published on Geo SCADA Knowledge Base by Anonymous user | June 10, 2021 05:11 AM
Architecture Flexibility
Geo SCADA Expert is the ideal base for your SCADA system, providing a wide range of architecture options and allowing the system to grow with your needs efficiently, economically and securely. This page describes our redundancy, scalability and flexibility - all without programming. Just configure and go!
Video Introduction
Please view this video to get an overview of the architecture options: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lmbMy4jJGX0
Lone Server Architecture
The simplest form of Geo SCADA Expert system is a Lone Server architecture. This involves a single server that runs independently, stores the database and communicates with the clients and hardware (outstations, PLCs and so on). There can be a client on the server as well as separate client PCs. 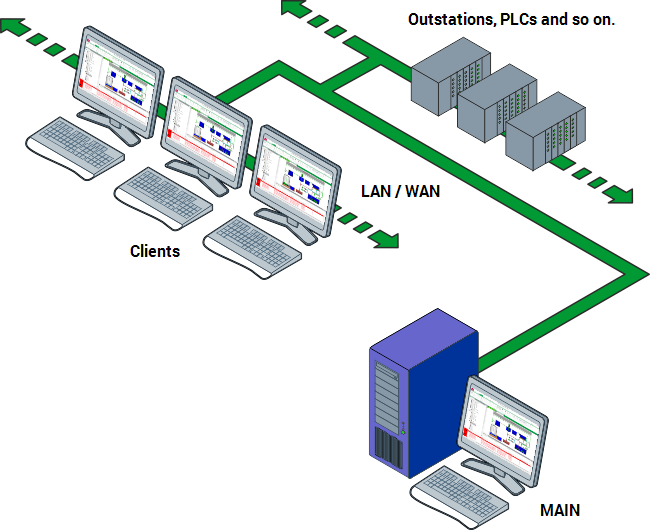
Hot-Standby Pair Architecture
Geo SCADA Expert offers more than most SCADA systems with it's simple and comprehensive synchronization features. Real-time data, Configuration and History are all synchronized to Standby servers.
A single configuration field is all that's needed to set up synchronization, and there are extra features such as supporting multiple redundant IP links and specifying network characteristics.
In a Hot-Standby Pair, one server acts as the Main server and the other server acts as a Standby server. The Main server runs the system drivers and acts as the primary server whereas the Standby server is used as a backup server.
The historian is synchronized, and administrators can configure the time window for that synchronization, which improves total synchronization time. 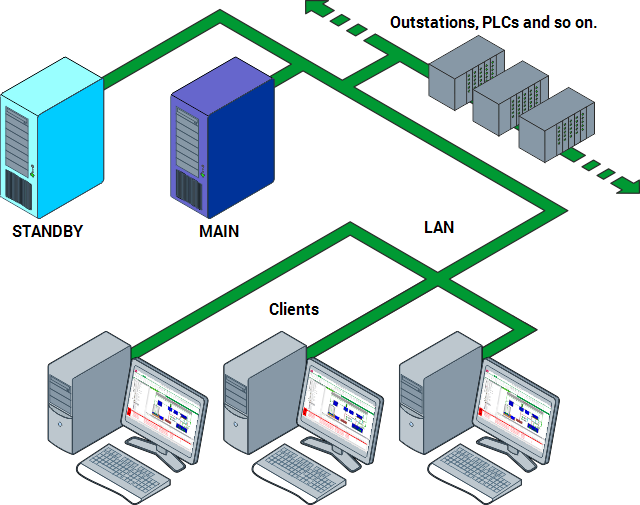
During synchronization, the Main server updates the Standby server. This process provides the Standby server with data and configuration that accurately represents the data on the Main server. So, if the Main server goes offline or there is a manual changeover, the Standby server can take over the duties of the Main server and the system will continue to run. When an offline server is able to resume normal operations, it communicates with the other server (which is now Main) and becomes the Standby server.
Client Connections
Clients automatically switch to the new Main server on changeover. All windows remain open, and the user remains logged in, so there is almost no interruption to operations during changeover.
Clients can be configured to connect to the closest server, for example when the Main and Standby A/B nodes are in separate locations with a WAN connection. This enables client performance to be faster, by reading data from a sever with faster network connection. For clients connected to Standby servers, Data modification actions are 'proxied' to the Main server to keep the database consistent. Clients connect to fully synchronized servers, but can be allowed to connect to part-synchronized servers which have configuration and real-time data and alarms but only the history left to synchronize.
Isolated Standby
If the Standby loses its connection with the Main server, a Main-Main situation can occur. This is when both servers act as Main servers because they cannot communicate with each other. There are various features which help you to control these situations:
- Network timeouts can be adjusted so that links can survive short disconnections
- On reconnection, the Main server which has been in the role longer (usually the Main at time of network break) will be the one resuming the role
- The servers 'ping' adjacent nodes such as network switches in order to determine whether the disconnection is a network problem or a server problem.
- If it is determined to be a network problem then the Standby is put into an '*Isolated Standby*' mode and will not attempt to be Main.
- An additional configuration option is to allow the Main-Main state to occur and use the 'Duty-Duty' feature which merges gathered data when the two servers reconnect and resume as Main and Standby.
Triple Standby Architecture
Triple Standby server architectures are similar to Hot-Standby pair architectures except that instead of there being one Standby server, there are two. As with Hot-Standby Pair arrangements, one of the servers is recognized as the Main server, with the other servers being Standby servers. Clients and plant can be connected to any of the servers, but the data they report is sent to the Main server and stored in the Main server's database. The Main server then updates the databases in the Standby servers so that they match the Main server database. 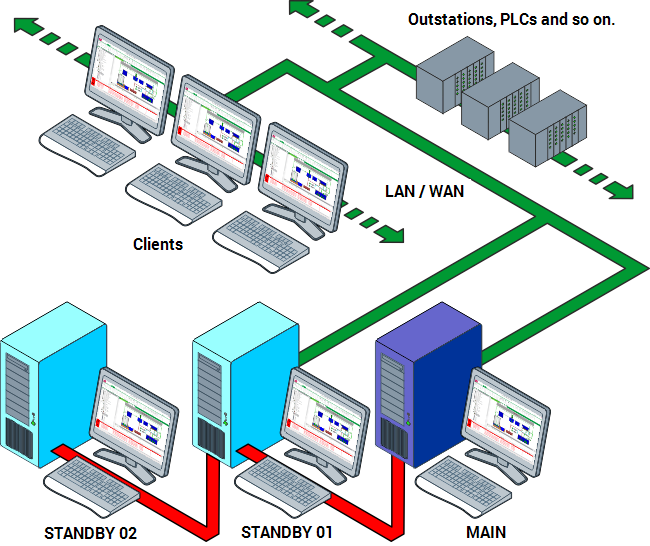
If the Main server loses its connections with both of the other servers but the other servers can still communicate with each other, the Main server will become isolated. The other two servers will arbitrate to determine which of the two is to switch to Main, and they will continue to run as a Hot-Standby Pair until the isolated server is restored. When the isolated server is able to connect to the other two servers, the three servers will arbitrate to determine which server is Main. The arbitration rules for the next Main server can be configured. The default is for the Standby server which has been running for the longest time will become the new Main server.
Features for client connections and server actions on isolation are similar to Hot Standby above.
Permanent Standby Server Architecture
Permanent Standby servers can only be set to Standby and are used as an additional part of a Hot-Standby Pair or Triple Standby architecture. Also known as 'Corporate Servers' or 'Standby Only' servers, Permanent Standby servers can reduce the demand placed on the Main and Standby servers in a multi-server architecture. Clients can work these Permanent Standby servers hard with data queries and not affect the Main or Standby servers.
A Permanent Standby server can be used:
As a 'performance firewall'---clients can connect to the system via the Permanent Server instead of the Main or Standby server, which reduces the demand on the Hot-Standby Pair's resources.
To improve performance for clients. This applies to read operations where the clients would have to connect to the Standby server over a slow WAN. Instead of reading data from the Standby server, the clients can be connected to the Permanent Standby locally---they can read the data from the Permanent Standby instead of the Standby and so avoid the need to use the WAN.
To increase the amount of historic data that is available online. By configuring a Permanent Server to store more historic data online, you can increase the amount of historic data that is available online without affecting the Main and Standby server's resources. For example, a Permanent Standby server can be configured to store historic data online for 5 years while the Main and Standby servers can be configured to store historic data online for only 1 year.
It is also possible to configure clients so that they connect to the Permanent Standby in preference to the other servers
A Permanent Standby server can be used:
- As a 'performance firewall'---clients can connect to the system via the Permanent Server instead of the Main or Standby server, which reduces the demand on the Hot-Standby Pair's resources.
- To improve performance for clients. This applies to read operations where the clients would have to connect to the Standby server over a slow WAN. Instead of reading data from the Standby server, the clients can be connected to the Permanent Standby locally---they can read the data from the Permanent Standby instead of the Standby and so avoid the need to use the WAN.
- To increase the amount of historic data that is available online. By configuring a Permanent Server to store more historic data online, you can increase the amount of historic data that is available online without affecting the Main and Standby server's resources. For example, a Permanent Standby server can be configured to store historic data online for 5 years while the Main and Standby servers can be configured to store historic data online for only 1 year.
It is also possible to configure clients so that they connect to the Permanent Standby in preference to the other servers
Geo SCADA Expert allows you to connect up to four Permanent Standby servers to a Hot Standby Pair architecture or up to three Permanent Standby servers to a Triple Standby architecture. Typically, a system that uses Permanent Standby servers is set up as follows:
- Clients that are used by operators and engineers are connected to a Hot-Standby Pair or Triple Standby architecture. As these are the users that use the system to monitor and control plant, they need to have a larger amount of system resources available so that they can react quickly and efficiently to 'real-life' situations on site.
- Clients that are used by managers, administrators and analysts are connected to a Permanent Standby server. This provides access to the data on the system without placing a high demand on the resources of the Main and Standby servers. So managers, administrators and analysts can access the system data and statistics without affecting the load on the Main and Standby servers.
In the setup shown in the following diagram, two Permanent Standby servers are used to reduce the load on the Main server and Standby server. The load is reduced by having the majority of users access the system via the Permanent Standby servers with fewer users accessing via the Main and Standby servers. 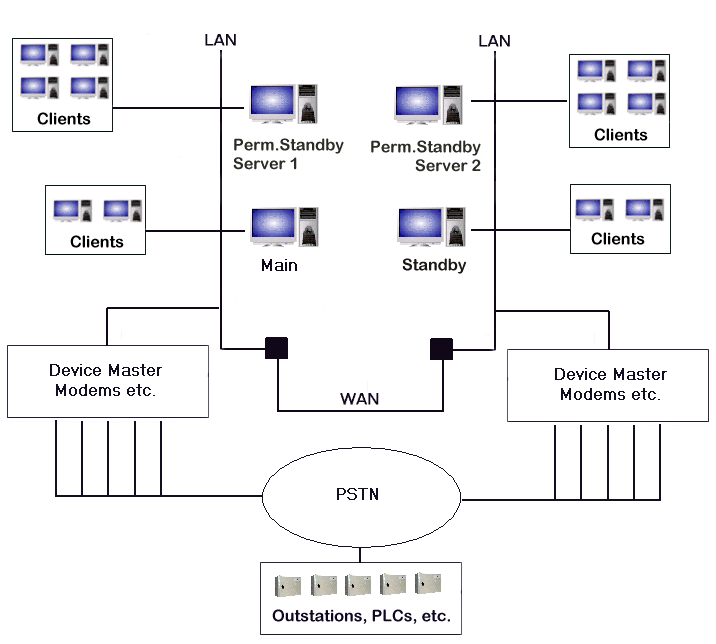
On some systems, Permanent Standby servers are also used to store large amounts of historic data. This is an effective way of making data available to users without using the resources of the Main and Standby servers.
Additional Security for Permanent Standby
Configuration settings allow for client PCs connecting to Permanent Standby servers to have a different, usually reduced, set of security permissions from those allocated when connecting to Main or Standby. For example, this may limit Control operations only to those clients connected to Main and Standby servers.
There is also an operating mode option for Permanent Standby servers called 'DMZ Permanent Standby' which has two effects:
- TCP connections between Main and Permanent Standby server are only ever initiated from the Main server
- Database writes are blocked from clients connected to Permanent Standby servers, even if the user would have had permission for the operation.
Scale Up - Each individual Geo SCADA Expert server can scale up to 1,000,000 points
Multiple Systems Architecture
Scale Out - Add more Geo SCADA Expert systems to expand and/or distribute the system
Geo SCADA Expert clients - ViewX and Virtual ViewX - are able to connect to Multiple server systems simultaneously. This allows architectures to be created such as having multiple remote systems accessible from one or more clients.Each system can consist of any mix of Lone Server, Hot Standby system or Hot Standby with Permanent Standby systems. 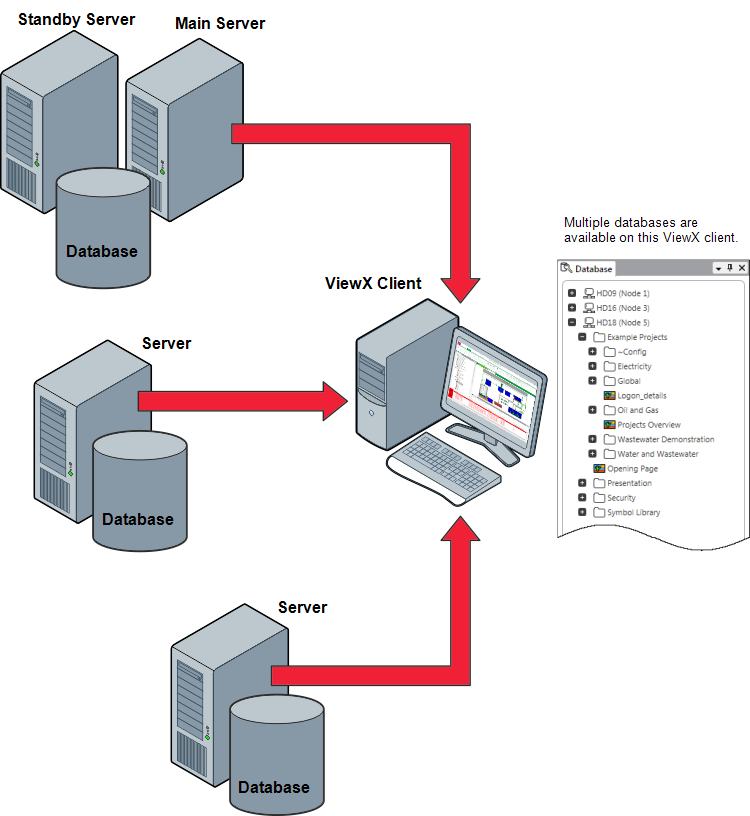
When users log in, they can choose to log in to just one server in the system or to multiple servers at the same time. When logging in to multiple servers the same credentials are used, but it is also possible to remain logged in to multiple servers with different credentials for each.
By expanding the system icons, you can reveal the hierarchical structures of each of the available databases. You can then access the various information, editing and configuration displays for each database item as required. You can also access information from multiple databases on a single display, for example, Mimics can contain dynamic data from items in different databases.
With a ViewX client that connects to multiple databases, you can:
Create, delete, and organize items in any of the available databases
Create, remove and modify security settings for items in any of the available databases
Configure and display Mimics that are stored in any of the available databases. The Mimics can be animated to display dynamic data from any of the available databases and can display dynamic data from different databases simultaneously
Configure and display Trends that contain data sourced from items in any of the available databases. Trends can display data from different databases simultaneously
Configure the items stored in any of the available databases, including database points, reports, and so on.
Access information displays for any item in any of the available databases
Display an Alarms List that shows alarms relating to items in any available database. The Alarms List can display alarms for multiple systems simultaneously and can be filtered to show individual databases, Groups, items, and so on,. too
By expanding the system icons, you can reveal the hierarchical structures of each of the available databases. You can then access the various information, editing and configuration displays for each database item as required. You can also access information from multiple databases on a single display, for example, Mimics can contain dynamic data from items in different databases.
With a ViewX client that connects to multiple databases, you can:
- Create, delete, and organize items in any of the available databases.
- Create, remove and modify security settings for items in any of the available databases.
- Configure and display Mimics that are stored in any of the available databases. The Mimics can be animated to display dynamic data from any of the available databases and can display dynamic data from different databases simultaneously.
- Configure and display Trends that contain data sourced from items in any of the available databases. Trends can display data from different databases simultaneously.
- Configure the items stored in any of the available databases, including database points, reports, and so on.
- Access information displays for any item in any of the available databases.
- Display an Alarms List that shows alarms relating to items in any available database. The Alarms List can display alarms for multiple systems simultaneously and can be filtered to show individual databases, Groups, items, and so on,. too.
Each system could be a similar size and architecture, to monitor local sites and 'see' sites from anywhere, or one could be a larger system, linked through this technology to multiple sites.
Hub and Spoke Architecture
Hierarchical Systems - collect and control both centrally and from satellite systems. Assign View and Control to users and servers.
All of the capabilities of Geo SCADA Expert can be mixed and matched to create a system suiting your business operation. This includes the capabilities for centralized access to configuration, alarm handling from different locations during the week, remote data gathering and aggregation centrally for reporting purposes, and the ability to be resilient to problems with networking. 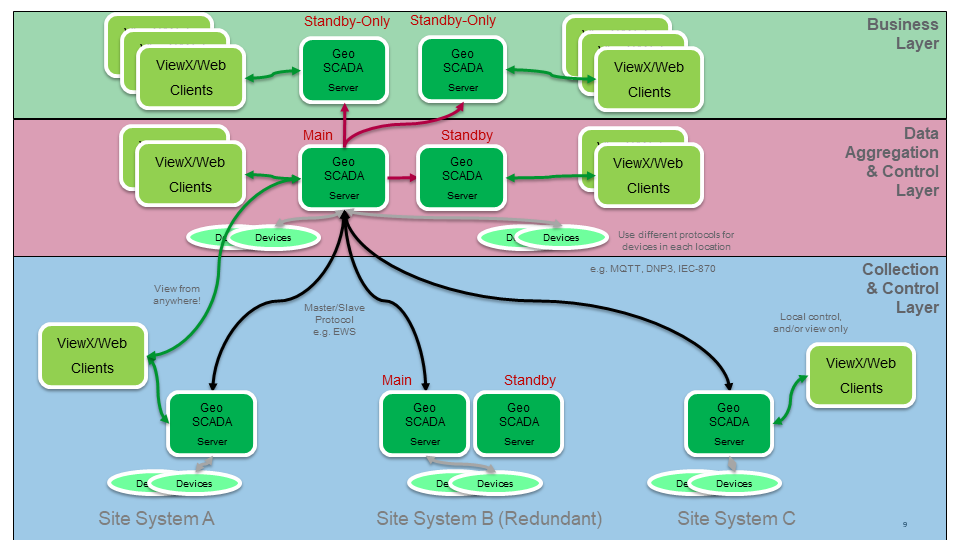
Multi-tier communications is supported natively by Geo SCADA Expert communication drivers, which give server capability as well as data gathering and control. These protocol servers are built in to Geo SCADA Expert and each allows data to be served to Geo SCADA's own drivers in an upper level system:
- Modbus
- DNP3
- IEC6-0870-101/4
- OPC-DA
- EWS - EcoStruxure Web Services
- Sparkplug
There is a detailed comparison of these on this site on the page: Comparison of Methods to Transfer Point Data Between ClearSCADA Systems.
All of these drivers and servers can be used with redundancy, allowing the upper tier server to automatically switch between communications links to the server or servers in the lower tier, so that dual servers at upper tier and lower tier and dual communications paths are available.
It is usually important to be able to back-fill data on communications, and to allow simple 'browse' capability when configuring the upper tier; therefore the use of the web service *EWS* is recommended for Hub and Spoke systems. EWS allows reading of real-time data as well as historic, with intelligent back-fill of historic data from the lower tier to upper.
Geo SCADA's drag-drop technology for configuration allows configuration objects to be easily copied between tiers and switched between protocol types. Therefore you will find it easy to build the configuration at each level with less effort.
Home
Author
Link copied. Please paste this link to share this article on your social media post.
Create your free account or log in to subscribe to the board - and gain access to more than 10,000+ support articles along with insights from experts and peers.

