Issue
When configuring a BBMD what is the Broadcast Distribution Mask and what are the valid settings for the field.
Product Line
EcoStruxure Building Operation, Continuum
Environment
- Building Operation Automation Server
- Building Operation Enterprise Server
- Continuum CyberStation
- bCX4xxx
Cause
Documentation
Resolution
When configuring a BBMD the BACnet protocol defines two methods of propagating the broadcasts messages to other networks.
The two methods are referred to as One-Hop also known as a Directed Broadcast and Two-Hop.
Note: In this article the subnet mask is shown using Classless Inter-Domain Routing(CIDR) notation. An IPV4 address is 32 bits long, CIDR notation defines the number of bits used for the subnet mask. The most commonly used are:
- /8 or 255.0.0.0
- /16 or 255.255.0.0
- /24 or 255.255.255.0
- /32 or 255.255.255.255
One-Hop
With the One-Hop method the local BBMD transfers the message directly to the remote devices via the remote router. In this case the IP routers have to support the transfer of IP broadcast messages to remote IP subnets
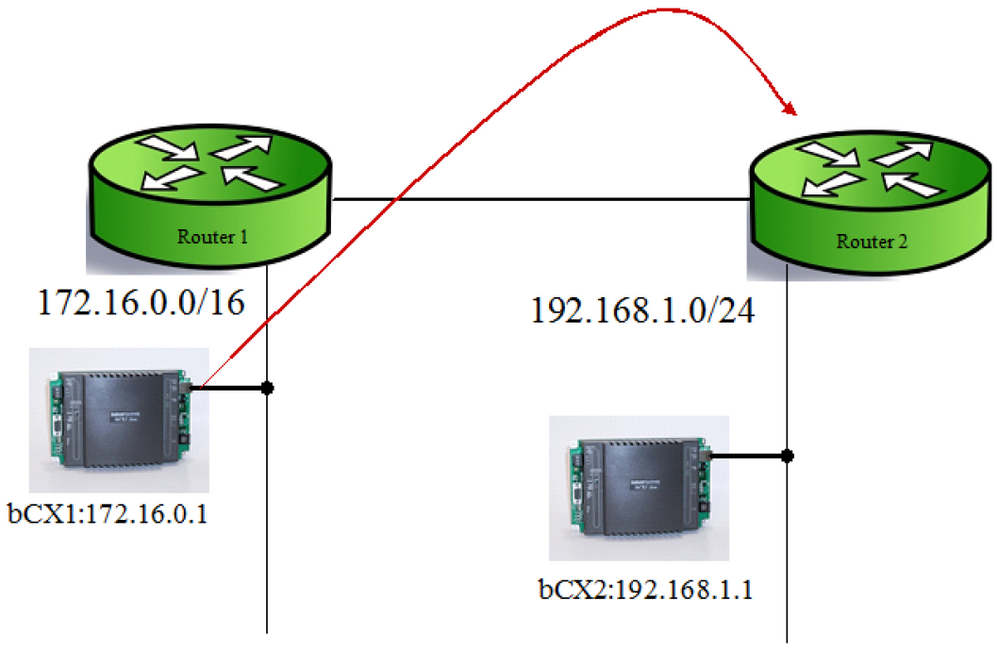
Figure 1 above illustrates the one-hop method, when the bCX1 which has been configured to take the role of BBMD for network 172.16.0.0/16 detects broadcast messages such as WHO-IS, I-AM etc, it sends a message directly to the broadcast address of the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet, it is then up to Router2 to send the directed broadcast to all devices on the subnet. Any device on the subnet that is acting as a router to other networks will then also re-broadcast the message on those networks. (i.e a bCX hosting an MSTP network on COMM2)
Two-Hop
With the Two-Hop procedure a BBMD device transfers broadcast messages to a further BBMD in the remote IP subnet, which then distributes the messages in its local network as IP broadcast messages for its IP subnet. Any device on the subnet that is acting as a router to other networks will then also re-broadcast the message on those networks.(i.e a bCX hosting an MSTP network on COMM2)
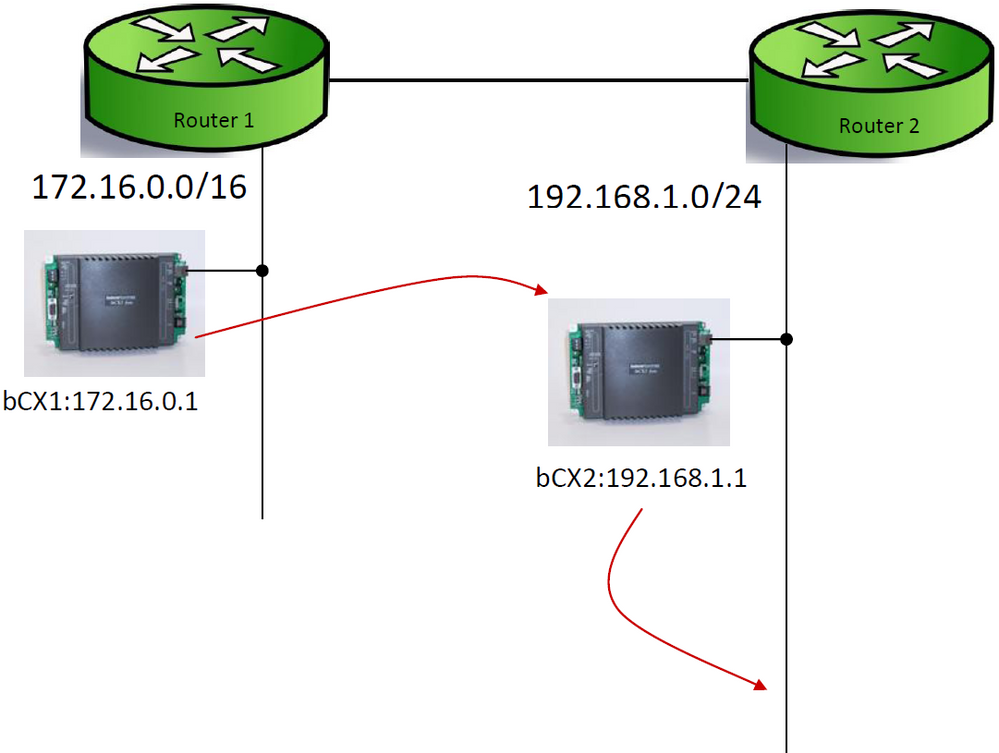
Figure 2 above illustrates the two-hop method, when the bCX1 which has been configured to take the role of BBMD for network 172.16.0.0/16 detects broadcast messages such as WHO-IS, I-AM etc, it sends a unicast message to each BBMD device on its table, it is then up to each BBMD device on each subnet to send a broadcast that will be heard by all devices on the subnet.
Which distribution mask should be used?
As mentioned earlier, in order for the one-hop method to work, the router on the remote subnet MUST be configured to process incoming messages sent to the broadcast IP address, the two-hop method on the other hand is guaranteed to work, so when in doubt use the two-hop method.
Most sites use two-hop distribution for the reason stated above,, the only obvious disadvantage of the two-hop method is that it is a little more verbose than the one-hop method since the message appears twice on the subnet, once as a unicast sent to the BBMD device and then again as a broadcast sent by the BBMD device.
In Building Operation and Continuum the distribution mask defaults to the two-hop method (/32 or 255.255.255.255)
How to configure the distribution mask
For one-hop enter the subnet mask of the remote network in the distribution mask, the system will apply the mask to the IP address to obtain the broadcast address for the remote network.
For two-hop enter 255.255.255.255, this tells the system not to do a direct broadcast and instead do a unicast to the remote BBMD device.
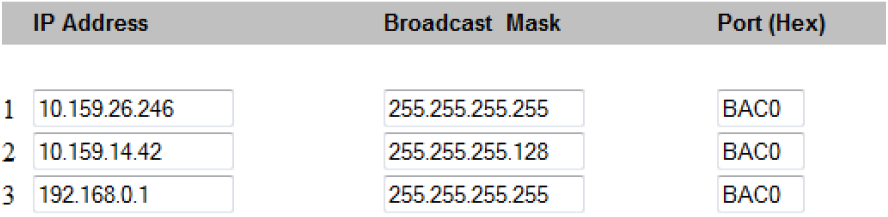
Sample distribution mask
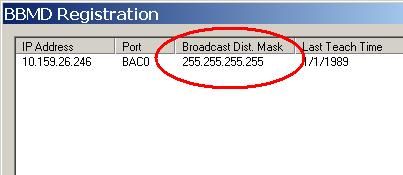
In the BBMD table of a bCX shown in the screen shot above, BDT #1 and #3 use the two-hop method while BDT entry #2 uses the one-hop method.