Issue
Converting the Velocity Pressure measured by the pressure sensor to Flow velocity (CFM)
Product Line
Andover Continuum,TAC INET,TAC Vista
Environment
Air flow measurement / balancing
Cause
Requirement for converting the velocity pressure to flow velocity (CFM)
Resolution
To calculate Air Flow in Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM), determine the Flow Velocity in feet per minute, then multiply this figure by the Duct Cross Sectional Area.
Air Flow in CFM (Q) = Flow Velocity in Feet Per Minute (V) x Duct Cross Sectional Area (A)
Determining Flow Velocity
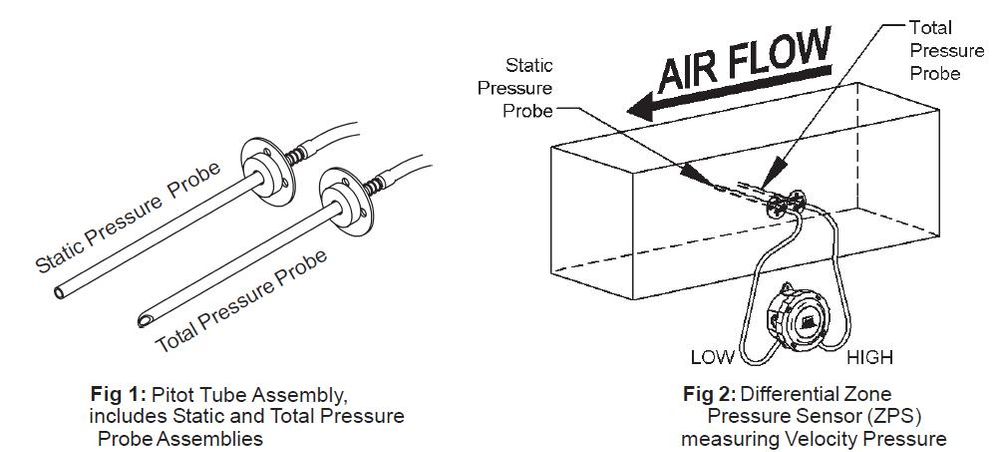
The easiest way to determine Flow Velocity is to measure the Velocity Pressure in the duct with a Pitot Tube Assembly connected to a differential pressure sensor. The Pitot Tube Assembly includes a Static Pressure Probe and a Total Pressure Probe. A Total Pressure Probe, aligned into the airflow, senses the duct velocity pressure and the static pressure, which equals the total pressure. A Static Pressure Probe aligned at a right angle to the airflow senses only the static pressure. The difference between the total pressure reading and the static pressure reading is the Velocity Pressure. If you connect the Total Pressure Probe to the HIGH port on a differential pressure sensor and the Static Pressure Probe to the LOW port on the differential pressure sensor, then the sensor’s output will be the Velocity Pressure, as shown in the figures below.
The Flow Velocity is then determined with the following equation:
V = 4005 x Sqrt(ΔP)
V = Flow Velocity in feet per minute.
Sqrt() = Square root of the number in the parenthesis.
ΔP = The Velocity Pressure measured by the pressure sensor
Example: Measuring a Velocity Pressure of .75” W.C. equals a Flow Velocity of 3,468 Ft/Min.
V = 4005 x Sqrt(0.75)
Sqrt(0.75) = 0.866 • 4005 x 0.866 = 3,468 • Flow Velocity = 3,468 Ft/Min
Determining Duct Cross Sectional Area
After obtaining the Flow Velocity from the previous procedure, that figure is now multiplied by the Duct Cross Sectional Area to determine the Air Flow in CFM.
There are two different equations for determining the Duct Cross Sectional Area, one for round ducts and one for square or rectangular ducts.
The equation for a round duct is:
A = π x r2
A = Duct Cross Sectional Area
π = 3.14159
r = radius of duct in feet
The equation for square or rectangular ducts is:
A = X x Y
A = Duct Cross Sectional Area
X = Duct height in feet
Y = Duct width in feet.
Example: An 18” diameter round duct has a Duct Cross Sectional Area of 1.77 Ft2
A = π x r2 or A = 3.14158 x .5625
18” diameter is 1.5 feet, therefore the radius is .75 feet • r2 = 0.752 = 0.5265 • π = 3.14159
A = 3.14159 x 0.5625 = 1.77 Ft2
Determining Air Flow in CFM
After obtaining the Flow Velocity and the Duct Cross Sectional Area from the previous two procedures, the Air Flow in CFM is determined by multiplying the two:
Air Flow in CFM (Q) = Flow Velocity in Feet Per Minute (V) x Duct Cross Sectional Area (A)
Example
An 18” diameter round duct with a Velocity Pressure of .75” W.C. has an Air Flow of 6,128 CFM
The Flow Velocity is 3,468 Ft/Min.
V = 4005 x Sqrt(ΔP)
V = 4005 x Sqrt(0.75)
Sqrt(0.75) = 0.866 • 4005 x 0.866 = 3,468 • Flow Velocity = 3,468 Ft/Min
The Duct Cross Sectional Area is 1.65 Ft2
A = π x r2
π = 3.14159 • r2 = 0.752 = 0.5625
Duct Cross Sectional Area (A) = 3.14159 x 0.5625 = 1.77 Ft2
The Air Flow in CFM is 6,128 Ft3/Min
Air Flow in CFM (Q) = Flow Velocity in Feet Per Minute (V) x Duct Cross Sectional Area (A)
Air Flow in CFM (Q) = 3,468 Ft/Min x 1.77 Ft2 = 6,128 CFM