Issue
What are VOCs and which ones are detected by our SLA/SLP sensor?
Product Line
Field devices
Environment
SpaceLogic SLA series and SpaceLogic SLP Series VOC Sensors
Cause
Unsure what substances are detected by the Space Logic SLA/SLP VOC sensors
Resolution
What are VOCs?
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs*) are a wide range of carbon based (organic) chemicals (compounds) found in various man-made and naturally occurring solids and liquids.
They evaporate easily at ordinary room temperature** which is why they are termed volatile.
VOCs are numerous, varied, and ubiquitous.
They include both human-made and naturally occurring chemical compounds. Most scents or odors are of VOCs. Some VOCs are dangerous to human health or cause harm to the environment. Respiratory, allergic, or immune effects in infants or children are associated with man-made VOCs and other indoor or outdoor air pollutants.
Government regulations have prompted several companies in the paint and adhesive industries to adapt with VOC level reductions in their products.
* VOCs play an important role in communication between plants, and messages from plants to animals.
** For example, formaldehyde, which evaporates from paint and releases from materials like resin, has a boiling point of only –19 °C (–2 °F).

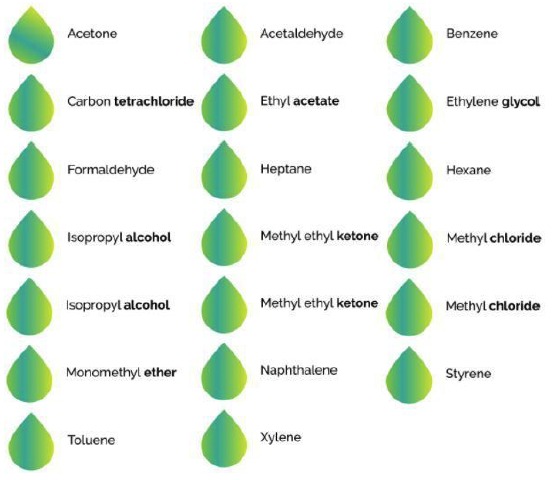
There are over 600 VOCs that can be found in the air. The following are commonly encountered in buildings:
Anthropogenic*** VOCs are regulated by law, especially indoors, where concentrations are the highest.
Harmful VOCs typically are not acutely toxic (result in throat irritation and headaches) but can have serious compounding long-term health effects(damage to internal organs).
Because the concentrations are usually low and the symptoms slow to develop, research into VOCs and their effects is difficult.
*** Relating or resulting from the influence of human beings on nature
How Are VOCs Measured?
VOC sensors normally present their measurement in Total Volatile Organic Compounds (TVOC) which corresponds to the sum of volatile organic compounds.
VOC contamination is an established concept in regulatory and scientific literature. It is a practical method (time and cost-effective) of surveying indoor environments for contamination.
The specific TVOC composition varies between different ambient indoor environments and indoor air is always composed of different volatile organic substances.
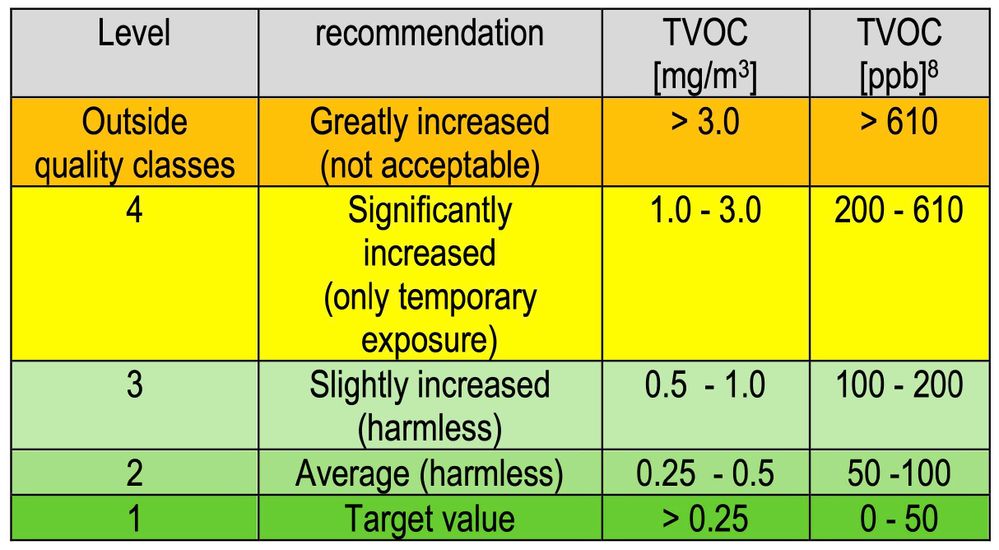
Therefore, it is helpful to consider TVOC concentrations as statistical reference values which help to indicate indoor air quality.
The World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines for TVOC are shown below and these are in line with the AQI table published in our specification sheets.
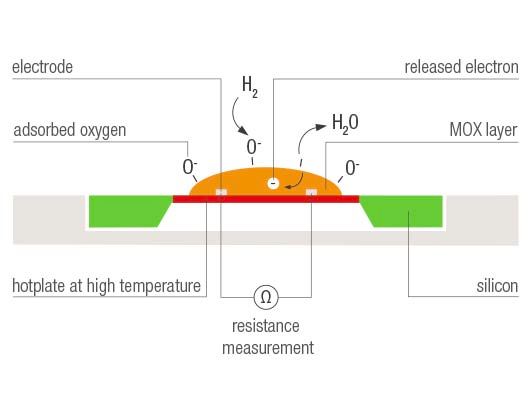
The sensing principle of the VOC sensor is based on a heated film of metal-oxide nano-particles.
In clean air, donor electrons in tin dioxide are attracted toward oxygen which is adsorbed on the surface of the sensing material, preventing electric current flow.
In the presence of reducing gases, the surface density of adsorbed oxygen decreases as it reacts with the reducing gases. Electrons are then released into the tin dioxide, allowing current to flow freely through the sensor.
VOC sensors are normally calibrated while using only one VOC (Ethanol).
Summary
There are over 600 identified VOCs that may be present in indoor air and the sensing element used by VOC sensors reacts to any of these compounds. Therefore it's not possible to state what VOC is responsible for a raised reading.